Study Notes on some facts about important island of the world (Part 2)
Victoria: An island in the Canadian Arctic. It is the 9th largest island in the world. The surrounding region is administered and supplied from Cambridge Bay on the island's south-east coast.
Ellesmere: It is the northern most island of Canadian Arctic and the third largest island in Canada. It was discovered in 1616 by William Baffin. Fort Conger was the base from which Robert Peary led the first expedition to reach the North Pole in 1909.
Sulawesi: Formerly known as Celebes, it is one of the four large islands of Indonesia. It is situated between Borneo and Maluku islands. In Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo, and Papua are larger in territory.
South New Zealand: Lying in the south Pacific, it is the largest island of New Zealand. It is dominated by the Southern Alps which stretch along its western coast and rise to 3764 m at Mt. Cook, New Zealand's highest peak. It was sighted by the Dutch navigator Tasman in 1642, and named after the Netherlands province of Zeeland.
Java: It is an island of Indonesia. With a population of about 137 million, it is the most populous island of the world. It is the home of to 60 per cent of Indonesia's population. Jakarta, the capital of Indonesia is located along the west Java. Formed mostly as the result of volcanic events, Java is the thirteenth largest island in the world and the 5th largest island in Indonesia. Its highest elevation (Semeru) is 3676 m.
North Island of New Zealand: Lying in the South Pacific, it is the second largest island of New Zealand. Active volcanism occurs in the central region of North Island, with many hot springs, and geysers.
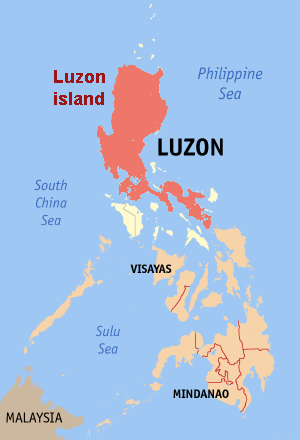
Luzon: It is the largest and economically and politically important island of Philippines. Manila, the capital of Philippines, is located on this island.
Newfoundland: The 16th largest island in the world, Newfoundland lies at the mouth St. Lawrence River, Canada. It was explored by John Cabot in 1497. It is a former colony of United Kingdom. It became the tenth province to the Confederation on 31st March, 1949, named simply as Newfoundland.
Cuba: Cuba, the largest island of Antilles, lies in the Caribbean Sea has a rainy, tropical climate. Sugarcane is the main crop of Cuba which occupies about 60 per cent of the cultivated land. Cubans call themselves 'Afro-Latin-Americans. Population of mixed descent (Mulattos) is 51 per cent, whites 37 per cent and blacks 11 per cent. Spanish is the main language. Havana, the capital and largest city of Cuba, is located on this island.

Iceland: Located between the North Atlantic and the Arctic Ocean, Iceland is an enormous plateau with an average altitude of 500 metres. Reykjavik is the capital and primate city of the country. About 96 per cent of Icelanders are the descendants of Norwegian, Scottish and Irish immigrants and are Protestants by faith.
Mindanao: It is the second largest and easternmost island of Philippines. The island of Mindanao is called The Land of Promise. Mindanao is the only area of Philippines with a significant Muslim population. A guerrilla war is ongoing on this island.
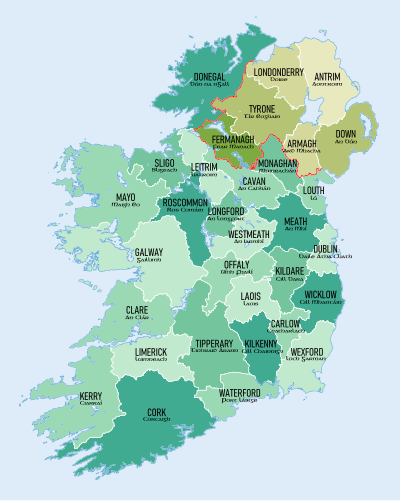
Ireland: An island of the British Isles lying west of Great Britain. Four - fifths of it is occupied by the Irish Republic, and remainder by Northern Ireland. Its economy rely heavily on agriculture, especially beef production and dairy farming, settled by Celts. Most of the people are Christians by faith.